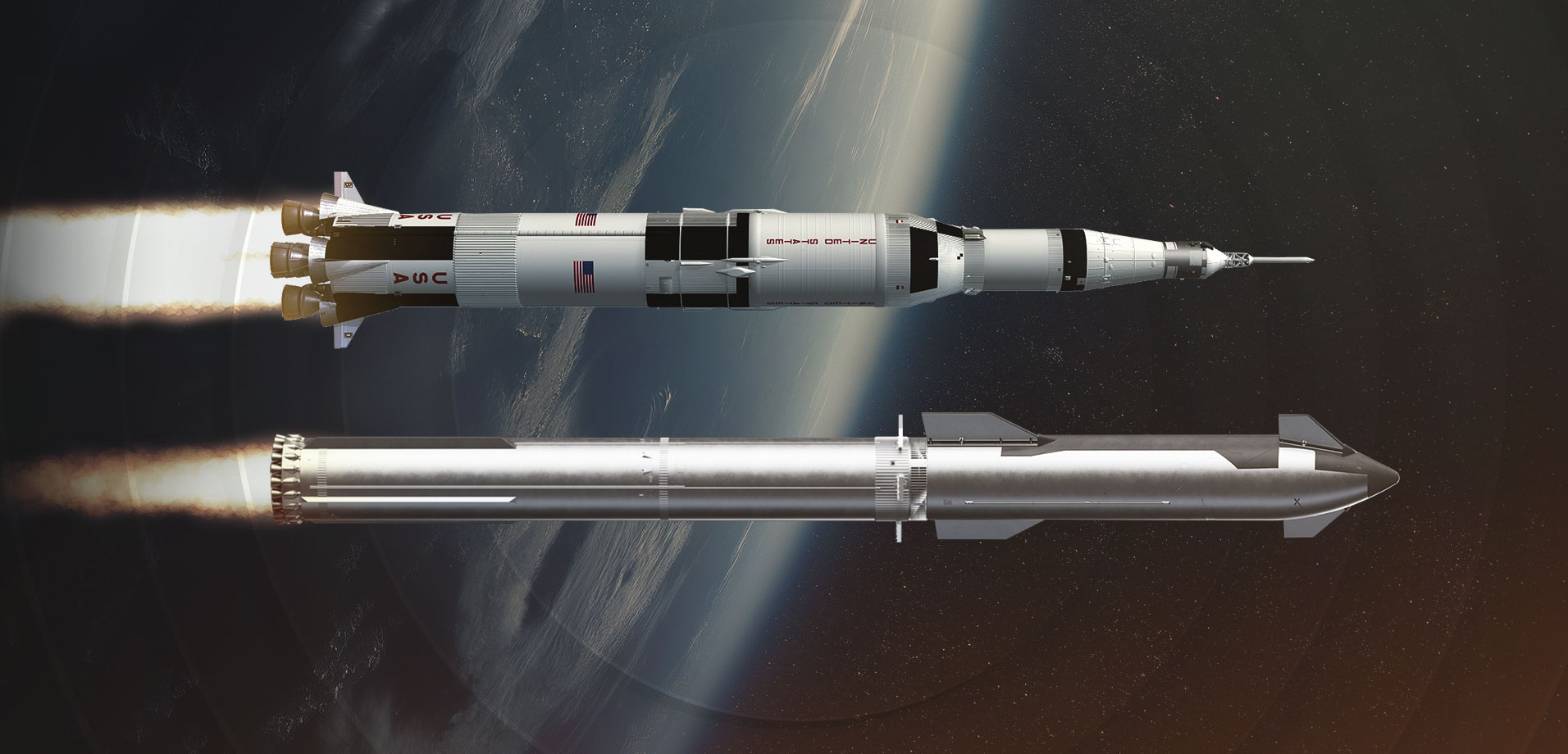
Starship vs Saturn V is a comparison of two of the most powerful rockets ever built. Saturn V was NASA’s moon rocket that carried astronauts during the Apollo missions, while Starship is SpaceX’s fully reusable next-generation launch system. While Saturn V holds the record for most powerful rocket by payload to orbit, Starship aims to surpass it with greater reusability, cost efficiency, and deep space ambitions.
Starship vs Saturn V
The race for space dominance has evolved dramatically over the decades, from the Cold War-driven Apollo era to the tech-powered modern age of private aerospace companies. Two rockets symbolize these eras: Saturn V, NASA’s mighty lunar rocket of the 1960s and 70s, and Starship, SpaceX’s futuristic vehicle designed to carry humans to Mars and beyond.
In this in-depth comparison, we will explore the differences and similarities between Starship vs Saturn V, breaking down everything from size, thrust, and payload to technology, cost, and long-term goals. Whether you’re a space enthusiast, a student, or just curious about the evolution of rocketry, this guide will provide clarity and insights.
Historical Context – A Rocket Built for the Moon vs One Aiming for Mars

Saturn V – The Apollo Era Titan
The Saturn V rocket was developed in the 1960s by NASA under the Apollo program. Designed by Wernher von Braun and his team, it was a response to President John F. Kennedy’s challenge to send a man to the Moon and return him safely to Earth before the end of the decade.
- First launch: 1967 (Apollo 4)
- Final mission: 1973 (Skylab 1)
- Missions: Apollo 11 (Moon landing), Apollo 17, Skylab
Saturn V stood as a symbol of American ingenuity and technological prowess during the space race.
Starship – SpaceX’s Vision for Interplanetary Travel
Starship, developed by SpaceX, is the most ambitious rocket ever created by a private company. It aims to be fully reusable and capable of carrying up to 100 people or over 100 metric tons of cargo into space.
- First integrated test flight: April 20, 2023
- Designed for: Earth orbit, Moon missions (Artemis), Mars colonization
- Reusable: Yes (both stages)
Starship is not just a rocket; it’s a system that includes the Super Heavy booster (first stage) and the Starship vehicle (second stage).
Size and Design Comparison
Height, Diameter, and Mass
| Specification | Saturn V | Starship + Super Heavy |
|---|---|---|
| Height | 363 feet (110.6 meters) | 394 feet (120 meters) |
| Diameter | 33 feet (10.1 meters) | 30 feet (9 meters) |
| Launch Mass | 6.5 million pounds | ~11 million pounds (est.) |
Key takeaway:
While Saturn V held the title of the tallest rocket for decades, Starship surpasses it in total height and is considerably heavier due to its stainless steel construction and massive propellant capacity.
Thrust and Performance
Thrust at Liftoff
- Saturn V: 7.6 million pounds-force (lbf)
- Starship (with Super Heavy): Up to 16.7 million lbf (based on current Raptor engine data)
Important note: Starship’s Raptor engines run on liquid methane and liquid oxygen (methalox), while Saturn V used kerosene (RP-1) and liquid hydrogen.
Payload to Orbit
| Metric | Saturn V | Starship |
|---|---|---|
| Payload to LEO | 140,000 lbs (63,500 kg) | 220,000 lbs (100,000 kg)+ |
| Payload to Moon | ~48,600 lbs (22,000 kg) | TBD (planned for Artemis) |
| Reusability | None | Fully reusable (goal) |
Bold fact:
Starship is designed to launch more payload than Saturn V at nearly half the cost per kilogram, primarily due to its reusability.
Cost and Reusability
Cost Per Launch
- Saturn V: ~$1.16 billion (adjusted for inflation)
- Starship: Targeting under $10 million per launch (SpaceX estimate)
Reusability Factor
Saturn V was completely expendable. Each rocket was used once and discarded after the mission. In contrast, Starship aims to be reused dozens of times, drastically reducing cost and waste.
This is a major leap in spaceflight economics, offering more frequent and affordable access to space.
Purpose and Missions
Saturn V’s Accomplishments
- First crewed lunar landing (Apollo 11)
- Multiple Moon missions (Apollo 12–17)
- Delivered Skylab (America’s first space station)
Saturn V had an impressive 100% success rate for crewed missions, making it one of the most reliable rockets in history.
Starship’s Future Plans
- Artemis program (NASA) – lunar lander variant selected
- Mars colonization – SpaceX’s primary goal
- Satellite deployment, space tourism, lunar base support
Elon Musk’s ultimate vision is to establish a self-sustaining colony on Mars, and Starship is the tool to achieve that.
Technology Comparison
Materials and Construction
- Saturn V: Used aluminum and traditional aerospace materials
- Starship: Made from stainless steel, chosen for durability, strength at cryogenic temps, and cost-efficiency
Engines
- Saturn V: Used five F-1 engines (first stage) – the most powerful single-chamber liquid-fuel engines ever
- Starship: Uses 33 Raptor engines on the Super Heavy booster and 6 on the Starship vehicle
Raptor engines offer advanced control, deep-throttling, and higher specific impulse compared to F-1s.
Environmental Impact
Starship’s methane-fueled Raptor engines produce less soot than traditional RP-1-based rockets like Saturn V, making it a cleaner choice for frequent space launches.
Additionally, reusability reduces the need for manufacturing new rockets every time, lowering overall carbon impact.
Conclusion – Starship or Saturn V?
The Starship vs Saturn V debate is not about which is better, but about how far rocket science has come. Saturn V remains a legendary engineering feat that helped humans reach the Moon. But Starship represents the next evolution – a sustainable, scalable way to explore the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
In summary:
- Saturn V was historic and powerful, but expensive and non-reusable.
- Starship is larger, stronger, cheaper, and reusable, designed with the future in mind.
Enjoyed this breakdown of Starship vs Saturn V?
👉 Share this article with fellow space fans,
👉 Subscribe to our newsletter for more space comparisons and updates,
👉 Or explore more on NewsNominal.com where we dive deep into the evolving world of space tech.
FAQ: Starship vs Saturn V
1. Which rocket is more powerful, Starship or Saturn V?
Starship is more powerful than Saturn V in terms of thrust, with over 16 million pounds-force compared to Saturn V’s 7.6 million. However, Saturn V still holds records for successful crewed missions.
2. How much payload can Starship carry compared to Saturn V?
Starship can carry over 100 metric tons to low Earth orbit, nearly double Saturn V’s capacity of 63.5 metric tons.
3. Is Starship reusable?
Yes, Starship is designed to be fully reusable, including both its booster and upper stage, unlike Saturn V which was expendable.
4. What is the purpose of Starship?
Starship aims to enable missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond. It’s also designed for satellite deployment, crewed spaceflight, and long-term colonization efforts.
5. Did Starship fly yet?
Yes, integrated Starship tests have taken place, with further developments and missions planned as part of NASA’s Artemis program and SpaceX’s Mars ambitions.